The ISO 56000 series of Innovation Management standards is a family of standards published by ISO (International Organisation for Standardisation), in collaboration with approximately 50 other countries, that is aimed at providing guidance to organisations on how to manage innovation better and benchmark their related activities and programmes.
It provides a baseline for effective innovation management as a business discipline in the professional world.
It is important to note that that these standards are written with the common High-Level Structure (HLS) of ISO Management System Standards and is enabling the integration of different ISO management systems. ISO 9001 adopted this structure in 2015 and when you look at activities like setting objectives, capturing data and data analysis these will integrate easily, as will the vast majority of the Innovation Standard.[1]
An Innovation Premium for your Organisation
It is a good idea to start to understand the ISO 56000 series of innovation management standards in order to manage innovation more successfully in your organisation, and to start preparing for certification. The real rationale however, would be to obtain an “innovation premium”. Understanding and adhering to the globally adopted Innovation Management standards will make your organisation more attractive to investors and will demonstrate a concrete and measurable understanding of the importance of innovation as a strategic lever for the future growth and sustainability of your organisation.1
The ISO 56000 Family of Innovation Management Standards
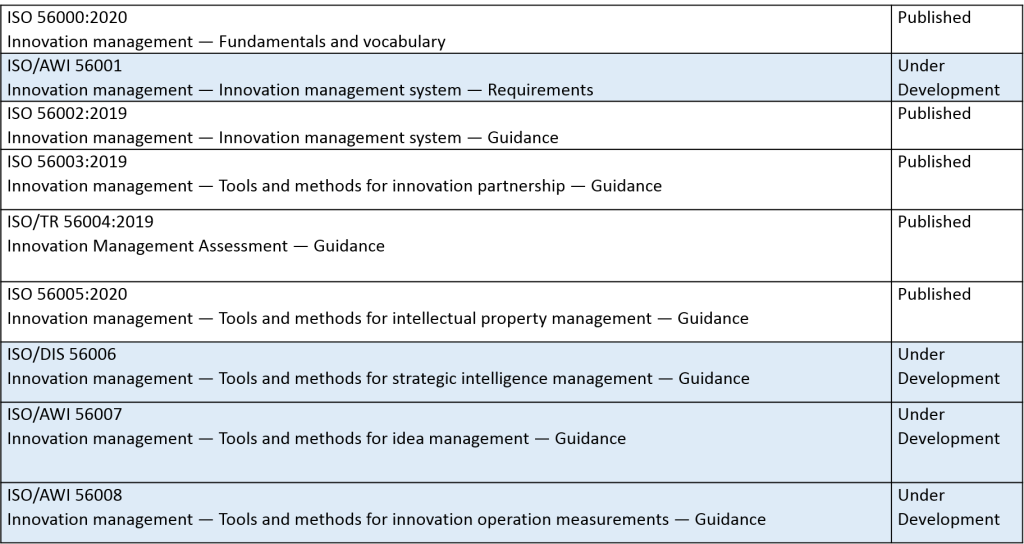
At a high-level, the ISO 56000 family contains the following standards, all of which can be purchased through the ISO store. Please check the ISO site regularly as these details change as standards move through the development process towards publication.
It is About Innovation Management as a System
The ISO work on the Innovation Management standards and guidelines adopts a systems approach. A systems approach to innovation management consider various interrelated elements that influences each other and interacts on the way innovation is managed, this again determines how outcomes will be affected. The ISO 560002 Innovation Management System standards is based on this understanding.
The standards on innovation management, will ultimately assist with capability development for organisations in innovation. It is designed to support innovation in organisations regardless of origin, type or size. It will lead to market, cultural and organisational benefits. ISO positions these benefits as follows:
Market Benefits
- Provide guidance on how an organization can fulfil unmet customer needs
- Increase business opportunities and open new markets
- Lead to the consequent reduction in trade barriers
- Reduce time to market
- Enhance the competitiveness of various organizations
- Answer to the need of both developed and emerging countries
Cultural Benefits
- Develop open‐mindedness to accept new business models and methods
- Promote the growth of an innovation culture with a global objective
- Facilitate the implementation of partnerships
- Improve collaboration and communication on a global scale
- Implement social responsibility in the organization’s innovation process
Organisational Benefits
- Save cost and reduce risk when innovating and collaborating across borders due to the development of standard tools
- Increase the organization ability to take decisions: test and try, fail fast, capability to take reasonable risks, facing challenges and world changes…
- Improve the efficiency and the performance of the organizations to produce innovation
- Improve results of innovation process and contributes to monitor the return of investments made in innovation
- Share a globally accepted ‘common language’ for innovation management
- Evaluate the progress of the organisation and identify and share good practices in innovation management
Below is a very high level view on the scope of the Innovation Management standards that have been published thus far and that have been adopted by the SABS (South African Bureau of Standards).
ISO 56000 or locally adopted as SANS 56000, Innovation management – Fundamentals and vocabulary, is the most recent of the eight-part series of standards and other guidance documents designed to help organisations use the correct terminology for innovation management. It provides the vocabulary, fundamental concepts and principles of innovation management, and is useful for organisations wanting to make their innovation management activities visible and credible.
The scope of ISO 56000/SANS 56000 is:
To provide the vocabulary, fundamental concepts and principles of innovation management and its systematic implementation. It specifies the terms and definitions applicable to all innovation management and innovation management system standards developed by ISO/TC 279.
It is applicable to:
- organisations implementing an innovation management system or performing innovation management assessments;
- organisations that need to improve their ability to effectively manage innovation activities;
- users, customers and other relevant interested parties (e.g. suppliers, partners, funding organizations, investors, universities and public authorities) seeking confidence in the innovation capabilities of an organization;
- organisations and interested parties seeking to improve communication through a common understanding of the vocabulary used in innovation management;
- providers of training in, assessment of, or consultancy for, innovation management and innovation management systems;
- developers of innovation management and related standards.
Aside from ISO 56000/SANS 56000, other ISO innovation management standards in the series published in 2019, includes the following:
- ISO 56002/SANS 56002, Innovation management – Innovation management system – Guidance
This standard provides guidance for the establishment, implementation, maintenance, and continual improvement of an innovation management system for use in all established organisations. It does not describe detailed activities within the organisation, but rather provides guidance at a general level. It also does not prescribe any requirements or specific tools or methods for innovation activities.
The ISO 56002/SANS 56002 standard presents guidance around 7 key elements for organisations to consider (Fig.1) when wanting to effectively manage and grow an innovation capability. These are:
- context,
- leadership,
- planning,
- support,
- operations,
- evaluation, and
- improvement
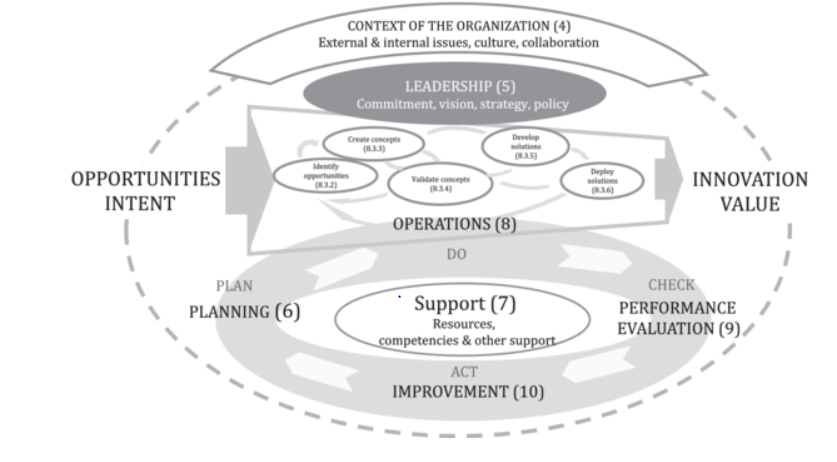
Figure 1: Representation of the framework of the innovation management system with references to the clauses of the document (Source: ISO.org)
It is further based on eight key innovation management principles.
The innovation management principles in the document includes a “statement of the principle, a rationale of why the principle is important for the organisation, some examples of benefits associated with the principle, and finally examples of actions the organisation can take to improve performance when applying the principle.” (Source: ISO.org)
The following principles are seen as the foundation of the innovation management system:
- realization of value;
- future-focused leaders;
- strategic direction;
- culture;
- exploiting insights;
- managing uncertainty;
- adaptability;
- systems approach.
- ISO 56003/SANS 56003, Innovation management – Tools and methods for innovation partnership – Guidance
The standard on innovation partnerships are developed to create value for each partner working together. It describes an innovation partnership framework and the sample corresponding tools to help organisations:
- decide whether to enter an innovation partnership,
- identify, evaluate and select partners,
- align the perceptions of value and challenges of the partnership,
- manage the partner interactions.
- ISO/TR 56004/SANS/TR 56004, Innovation management assessment – Guidance
This Technical Report helps users to understand why it is beneficial to carry out an Innovation Management Assessment (IMA). It gives guidance on:
- what to assess, and
- how to carry out the IMA, and thus maximize the resulting benefits.
These are universally applicable to:
- organisations seeking sustained success in their innovation activities;
- organisations performing IMAs;
- users and other interested parties (e.g. customers, suppliers, partners, funding organizations, universities and public authorities) seeking confidence in an organisation’s ability to manage innovation effectively;
- interested parties seeking to improve communication through a common understanding of Innovation Management (IM), via an assessment;
- providers of training, assessment, or advice in IM;
- developers of related standards;
- academics interested in research related to IMA.
Other ISO 56000 Innovation Management standards currently under development, but not yet published in the ISO 56000 series are:
- ISO 56005, Innovation management – Tools and methods for intellectual property management – Guidance
- ISO 56006, Innovation management – Strategic intelligence management – Guidance
- ISO 56007, Innovation management – Idea management
- ISO 56008, Innovation management – Tools and methods for innovation operation measurements – Guidance
Work on the Innovation Management standards is expected to be completed in the next two to three years.
The South African Bureau of Standards (SABS) are the custodians of the ISO 56000 series of Innovation Management Standards in South Africa. Please contact us here should you need any more information or assistance to integrate this thinking into your organisation.
Contact Innocentrix here if you need more information or if you are interested in on-line innovation management training or to attend a future (virtual) workshop.
Remember to consult the Innocentrix website for regular updates on the latest information with regards to the ISO 56000/SANS 56000 series of Innovation Management standards and progress in this regard.
[1] Taken from iso56000.com.

